The database that used as a storage is created manually and is populated using Storage.sql script from the Indeed CM installation package (.. \IndeedCM.Server\Misc).
Data storage creation
1. Create a database in SQL Management Studio environment with an arbitrary name (say, IndeedCM):
To do this, in the Object Explorer, right-click on the Databases tab and select New Database... . Specify the Database Name: for example, IndeedCM and click OK (Figure 2).
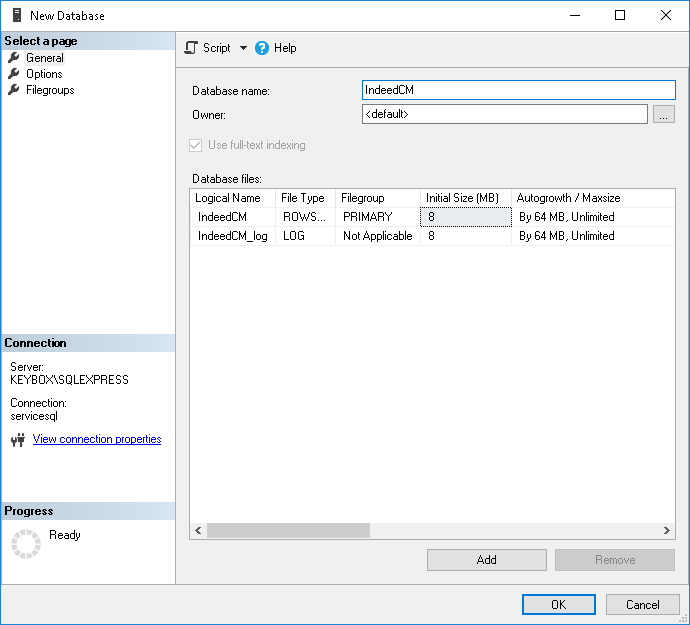
Figure 2 – Microsoft SQL: permissions for working with database.
2. Use a local SQL account or Windows domain account (for example, servicecm) and define the permissions for the created database. This account shall be used to perform reading data from the database and writing data to it. Connection of the account to the database is carried out with Indeed CM Setup Wizard.
- Define Logins for the created database (for example, servicecm):
Click Security > Logins, select an account from the list. Go to the User Mapping tab and grant permissions to work with the database for the selected login, specify permissions: db_owner and public and click OK (Figure 3).
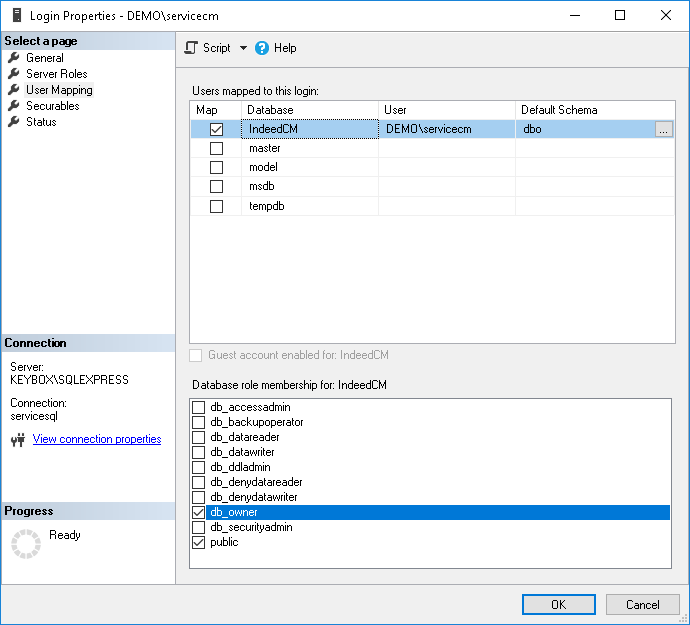
Figure 3 – Microsoft SQL: permissions for working with database.
3. Select the created database (IndeedCM) in the Object Explorer and execute the Storage.sql script:
- Choose File > Open > File... (or Ctrl+O), specify the path to the Storage.sql file (located in the ..\IndeedCM.Server\Misc directory) and click Open.
- Before executing the script, uncomment: --USE [<database name>] --GO and specify the name of the database for which the script is applied (IndeedCM): --USE [IndeedCM] --GO. Or select the required database in the drop-down menu (see Figure 4).
- Click Execute.
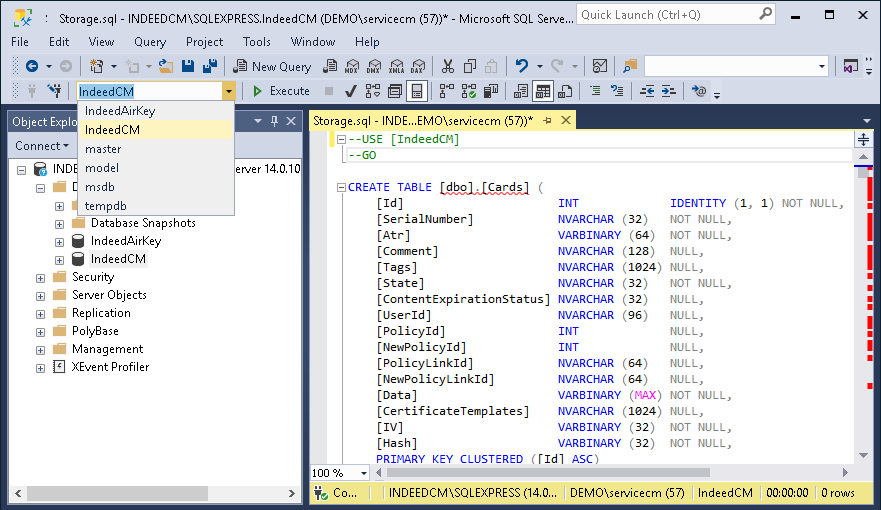
Figure 4 - Selecting a database to execute the script.
4. If Indeed CM Agent is used, set permissions on the CMAgentSessionType, UpdateAgentSession and UpdateAgentSessions objects of the created database (IndeedCM) for the service account (for example, servicecm):
- Open the Properties of the CMAgentSessionType object located path Programmability > Types > User-Defined Table Types.
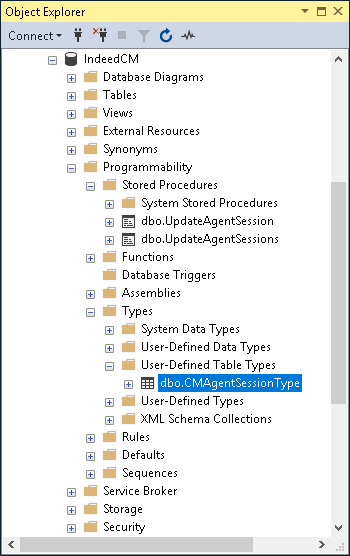
Figure 5 - The location of objects in the MS SQL database.
- Go to the Permissions tab, to search for a service account, click Search... .
- Issue Permissions for the selected account: to Control this object (Figure 6).
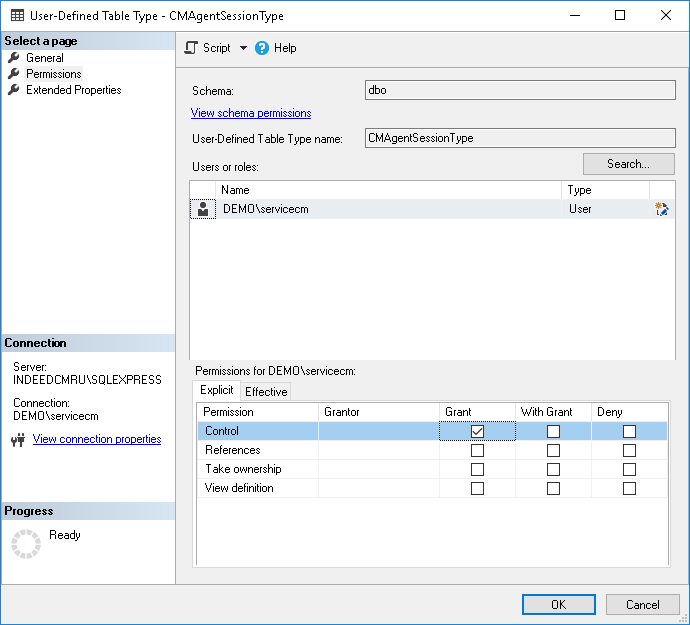
Figure 6 - Permissions for database objects.
- Similarly, set Execute permissions for UpdateAgentSession and UpdateAgentSessions objects located path Programmability > Stored Procedures.